Precision Time Protocol#
The IEEE 1588 standard defines the protocol. Basler cameras support IEEE 1588-2008, also known as PTP Version 2.
Info
The precision of the PTP synchronization depends to a large extent on your network hardware and setup. For maximum precision, choose high-quality network hardware, use PTP-enabled network switches, and add an external PTP clock device with a GPS receiver to your network.
Using the Feature#
Why Use PTP#
The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) feature enables a camera to use the following features, if available:
How It Works#
Through PTP, multiple devices (e.g., cameras) are automatically synchronized with the most accurate clock found in a network, the so-called master clock or best master clock.
The protocol enables systems within a network to do the following:
- Synchronize with the master clock, i.e., set the local clock as precisely as possible to the time of the master clock.
- Syntonize with the master clock, i.e., adjust the frequency of the local clock to the frequency of the master clock. You want the duration of a second to be as identical as possible on both devices.
The master clock is determined by several criteria. The criterion with the highest precedence is the device's Priority 1 setting.
Timestamp Synchronization#
The basic concept of the Precision Time Protocol (IEEE 1588) is based on the exchange of PTP messages. These messages allow the slave clocks to synchronize their timestamp value with the timestamp value of the master clock. For Basler cameras, this means that their TimestampLatchValue parameter values will be as identical as possible. The precision highly depends on your network hardware and setup.
If no device in the network is synchronized to a coordinated world time (e.g., TAI or UTC), the network will operate in the arbitrary timescale mode (ARB). In this mode, the epoch is arbitrary, as it is not bound to an absolute time. The timescale is relative and only valid in this network.
Info
- IEEE 1588 defines 80-bit timestamps for storing and transporting time information. Because GigE Vision uses 64-bit timestamps, the PTP timestamps are mapped to the 64-bit timestamps of GigE Vision.
- A PTP-enabled device that operates in a network with no other PTP-enabled devices does not discipline its local clock. The precision of its local clock is identical to a non-PTP-enabled device.
- For more information about the Precision Time Protocol, see the Synchronous and in Real Time: Multi-Camera Applications in the GigE Network white paper.
Enabling PTP Clock Synchronization#
When powering on the camera, PTP is always disabled. If you want to use PTP, you must enable it.
To enable PTP:
- If you want to use an external device as the master clock (e.g., a GPS receiver), configure the external device as the master clock.
Basler recommends an ANNOUNCE interval of 2 seconds and a SYNC interval of 0.5 seconds. - Make sure that all cameras that you want to synchronize via PTP are properly configured.
- On all cameras that you want to synchronize via PTP, set the
GevIEEE1588parameter totrue. - Wait until all PTP network devices are sufficiently synchronized. Depending on your network setup, this may take a few seconds or minutes.
You can determine when the devices are synchronized by checking the status of the PTP clock synchronization.
Now, you can use the PTP-enabled camera features.
Info
On ace Classic/U/L cameras, enabling PTP clock synchronization changes the camera's internal tick frequency from 125 MHz (= 8 ns tick duration) to 1 GHz (= 1 ns tick duration). The Inter-packet Delay and the Frame Transmission Delay parameter values are adjusted automatically.
On other cameras, the tick frequency is always 1 GHz.
Configuring PTP Clock Synchronization#
Depending on your camera model, the following settings are available:
Priority 1#
In a PTP-enabled network, the master clock is determined by several criteria. The most important criterion is the device's Priority 1 setting. The network device with the lowest Priority 1 setting is the master clock.
On ace 2 and dart M cameras, you can change the Priority 1 setting to force a camera to be the master clock, or to prevent a camera from being the master clock. To do so, set the BslPtpPriority1 parameter to a value between 0 (highest priority) and 255 (lowest priority).
On other cameras, the Priority 1 setting is preset to 128 and can't be changed.
Info
For more information about the master clock criteria, see the IEEE 1588-2008 specification, clause 7.6.2.2.
PTP Delay Mechanism#
The delay measurement mechanism defines how PTP delay measurement messages are sent and received within the network. The PTP standard defines two mechanisms: end-to-end (E2E, also "delay request-response") and peer-to-peer (P2P). For more information, see this article.
On ace 2 and dart M cameras, you can change the delay measurement mechanism. To do so, set the BslPtpProfile parameter to DelayRequestResponseDefaultProfile (default) or PeerToPeerDefaultProfile.
On other cameras, the delay measurement mechanism is preset to end-to-end and can't be changed.
Info
- In most cases, use end-to-end delay measurement. Only use peer-to-peer if your entire network is set up for peer-to-peer delay measurement. This means that all switches and routers are PTP-enabled, and all PTP devices are configured for peer-to-peer communication.
- When using peer-to-peer delay measurement, the following restrictions apply:
- The network mode can't be set to Hybrid.
- One-step clock operation can't be enabled. The camera always operates in two-step mode.
Network Mode#
The network mode setting defines how PTP messages are transferred within the network.
On ace 2 cameras, you can change the network mode. To do so, set the BslPtpNetworkMode parameter to one of the following values:
Multicast: PTP messages are sent to all devices in the local network that are configured for PTP multicasting. This is the default mode and sufficient for most use cases.Hybrid: PTP messages are sent using multicast and unicast messages. This saves network load because fewer messages have to be processed. For more information, see this article.Unicast: PTP messages are sent to one or more specified devices in the local network. Other devices can't receive PTP messages.
To configure unicast:- Make sure that the
BslPtpNetworkModeis set toUnicast. - Set the
BslPtpUcPortAddrIndexparameter to 0. - Set the
BslPtpUcPortAddrparameter to the IP address of the first receiving device. - Increase the
BslPtpUcPortAddrIndexparameter by 1. - Set the
BslPtpUcPortAddrparameter to the IP address of the next receiving device. - Repeat steps 3 and 4 for all PTP devices involved.
- Make sure that the
On other cameras, the network mode is preset to multicast. However, these cameras can also receive unicast messages and respond accordingly.
Info
When using unicast mode, all devices involved must support unicast negotiation. Some PTP implementations don't use unicast negotiation and therefore aren't compatible with Basler cameras.
PTP Management#
The PTP Management Protocol allows you to read the settings of any PTP device via management messages, i.e., without using the pylon API. If permitted, the settings can also be written.
On ace 2 and dart M cameras, you can enable or disable PTP management. To do so:
- Enable PTP clock synchronization.
- Set the
BslPtpManagementEnableparameter to one of the following values:true: You can read settings (GET), write settings (SET), and execute commands (COMMAND) using management messages with the message IDs listed below.false(default): The PTP Management Protocol is disabled, and settings can neither be read nor written.
On other cameras, PTP management is always enabled and preset to read-only access.
Supported Management Messages#
| Management Message ID | Supported Action |
|---|---|
| NULL_MANAGEMENT | GET, SET |
| CLOCK_DESCRIPTION | GET |
| USER_DESCRIPTION | GET, SET |
| INITIALIZE | COMMANDa |
| DEFAULT_DATA_SET | GET |
| CURRENT_DATA_SET | GET |
| PARENT_DATA_SET | GET |
| TIME_PROPERTIES_DATA_SET | GET |
| PORT_DATA_SET | GET |
| PRIORITY1 | GET, SET |
| PRIORITY2 | GET, SET |
| DOMAIN | GET |
| SLAVE_ONLY | GET |
| LOG_ANNOUNCE_INTERVAL | GET, SET |
| ANNOUNCE_RECEIPT_TIMEOUT | GET, SET |
| LOG_SYNC_INTERVAL | GET, SET |
| VERSION_NUMBER | GET |
| ENABLE_PORT | COMMAND |
| DISABLE_PORT | COMMAND |
| TIME | GET, SETb |
| CLOCK_ACCURACY | GET, SET |
| UTC_PROPERTIES | GET, SET |
| TRACEABLE_PROPERTIES | GET, SET |
| TIMESCALE_PROPERTIES | GET, SET |
| UNICAST_NEGOTIATION_ENABLE | GET |
| ACCEPTABLE_MASTER_TABLE | GET, SET |
| ACCEPTABLE_MASTER_TABLE_ENABLED | GET, SET |
| ACCEPTABLE_MASTER_MAX_TABLE_SIZE | GET |
| DELAY_MECHANISM | GET, SET |
| LOG_MIN_PDELAY_REQ_INTERVAL | GET, SET |
-
The INITIALIZE command resets the clock speed.
-
Can only be set if the corresponding device serves as the grandmaster clock.
For information about the default values and ranges of these attributes, see the IEEE 1588-2008 specification, annex J.
One-Step or Two-Step Clock#
This setting defines how many messages are generated for any PTP event message that requires an egress timestamp:
- In one-step operation, one message is sent. The message includes the message data and the egress timestamp.
- In two-step operation, two messages are sent. The first message includes the message data. The second message includes the egress timestamp.
For more information, see this article.
On ace 2 and dart M cameras, two-step operation is disabled by default. If another PTP device in the network explicitly requires two-step event messages, you can enable them by setting the BslPtpTwoStep parameter to true.
On other cameras, two-step operation is always enabled.
Checking the Status of the PTP Clock Synchronization#
To check the status of the PTP clock synchronization, you must develop your own check method using the pylon API.
A typical implementation of a PTP status check involves the following steps:
- Execute the
GevIEEE1588DataSetLatchcommand.
The command allows you to take a "snapshot" of the camera's current PTP state. The "snapshot" implementation ensures that all parameter values in the latched data set refer to exactly the same point in time. - Wait until the
GevIEEE1588Statusparameter value is no longerInitializing. -
Depending on the camera model, read the following parameter values from the device:
- On ace 2 and dart M cameras, read the
PtpServoStatusparameter from all slave cameras. If the parameter value isLocked, the respective device should be sufficiently synchronized. If you need a more refined status check, follow the "other cameras" procedure below instead. -
On other cameras, read the
GevIEEE1588OffsetFromMasterparameter value from all slave cameras until the highest offset from master is below a certain threshold (according to your requirements, e.g., 1 millisecond).
Due to the fact that the clock is continuously adjusted by a control mechanism, the offset is not decreasing monotonically. Basler recommends that you check the maximumGevIEEE1588OffsetFromMasterparameter value within a given time window: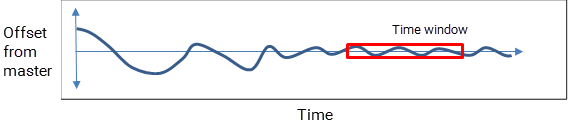
- On ace 2 and dart M cameras, read the
-
Repeat steps 1 and 2 until the devices are sufficiently synchronized.
What's In A Latched Data Set?#
After executing the GevIEEE1588DataSetLatch command, you can read the following parameter values from the device:
GevIEEE1588ClockId: Indicates the unique ID of the current PTP device (the "clock ID").GevIEEE1588OffsetFromMaster: Indicates the estimated temporal offset between the master clock and the clock of the current PTP device in ticks (1 tick = 1 nanosecond).GevIEEE1588ParentClockId: Indicates the clock ID of the PTP device that currently serves as the master clock (the "parent clock ID").GevIEEE1588Status: Indicates the state of the current PTP device, e.g., whether it is a master or a slave clock. The returned values match the PTP port state enumeration (Initializing, Faulty, Disabled, Listening, Pre_Master, Master, Passive, Uncalibrated, and Slave). For more information, refer to the pylon API documentation and the IEEE 1588-2008 specification.GevIEEE1588StatusLatched: If this parameter is available, Basler recommends using it instead of theGevIEEE1588Statusparameter. This is because theGevIEEE1588Statusparameter is not tied to theGevIEEE1588DataSetLatchcommand. Therefore, if you read multiple PTP-related values from a device, the device state will not relate to the same point in time as the other values.
Additional Parameters#
On ace 2 and dart M cameras, after executing the PtpDataSetLatch command, you can read the following additional parameter values from the device:
BslPtpDelayMechanism: Indicates the delay mechanism used by the PTP network. A value ofE2Eindicates that the Delay Request-Response mechanism is used. A value ofP2Pindicates that the peer-to-peer mechanism is used.PtpClockAccuracy: Indicates the expected accuracy of the PTP device clock when it is or becomes the grandmaster. On Basler cameras, the expected accuracy is preset toUnknown. This is because Basler cameras don't synchronize to a coordinated world time, e.g., UTC.PtpGrandmasterClockID: Indicates the clock ID of the PTP device that currently serves as the grandmaster clock.PtpServoStatus: Indicates the state of the clock servo, i.e., the state of the PTP clock synchronization. If the state isLocked, the clock of the current device is successfully synchronized with the master clock. In all other cases, the state isUnknown.
External Links#
- End-to-End Versus Peer-to-Peer (Time Synchronization Blog)
- Hybrid Mode PTP: Mixed Multicast and Unicast (Time Synchronization Blog)
- IEEE 1588-2008 Specification (IEEE Standards Association)
- One-step or Two-step? (Time Synchronization Blog)
- Precision Time Protocol (Wikipedia)
- White Paper: Synchronous and in Real Time: Multi-Camera Applications in the GigE Network (Basler)
Sample Code#
ace 2 Cameras#
// ** Configure PTP **
// Set Priority 1 to 128
camera.BslPtpPriority1.SetValue(128);
// Enable end-to-end delay measurement
camera.BslPtpProfile.SetValue(BslPtpProfile_DelayRequestResponseDefaultProfile);
// Set the network mode to unicast
camera.BslPtpNetworkMode.SetValue(BslPtpNetworkMode_Unicast);
// Set the IP address of the first unicast device to 192.168.10.12
// (0xC0 = 192, 0xA8 = 168, 0x0A = 10, 0x0C = 12)
camera.BslPtpUcPortAddrIndex.SetValue(0);
camera.BslPtpUcPortAddr.SetValue((0xC0A80A0C);
// Enable PTP Management Protocol
camera.BslPtpManagementEnable.SetValue(true);
// Disable two-step operation
camera.BslPtpTwoStep.SetValue(false);
// ** Enable PTP on the current device **
camera.PtpEnable.SetValue(true);
// To check the status of the PTP clock synchronization,
// implement your own check method here.
// For guidelines, see "Checking the Status of
// the PTP Clock Synchronization" in this topic.
INodeMap& nodemap = camera.GetNodeMap();
// ** Configure PTP **
// Set Priority 1 to 128
CIntegerParameter(nodemap, "BslPtpPriority1").SetValue(128);
// Enable end-to-end delay measurement
CEnumParameter(nodemap, "BslPtpProfile").SetValue("DelayRequestResponseDefaultProfile");
// Set the network mode to unicast
CEnumParameter(nodemap, "BslPtpNetworkMode").SetValue("Unicast");
// Set the IP address of the first unicast device to 192.168.10.12
// (0xC0 = 192, 0xA8 = 168, 0x0A = 10, 0x0C = 12)
CIntegerParameter(nodemap, "BslPtpUcPortAddrIndex").SetValue(0);
CIntegerParameter(nodemap, "BslPtpUcPortAddr").SetValue(0xC0A80A0C);
// Enable PTP Management Protocol
CBooleanParameter(nodemap, "BslPtpManagementEnable").SetValue(true);
// Disable two-step operation
CBooleanParameter(nodemap, "BslPtpTwoStep").SetValue(false);
// ** Enable PTP on the current device **
CBooleanParameter(nodemap, "PtpEnable").SetValue(true);
// To check the status of the PTP clock synchronization,
// implement your own check method here.
// For guidelines, see "Checking the Status of
// the PTP Clock Synchronization" in this topic.
// ** Configure PTP **
// Set Priority 1 to 128
camera.Parameters[PLCamera.BslPtpPriority1].SetValue(128);
// Enable end-to-end delay measurement
camera.Parameters[PLCamera.BslPtpProfile].SetValue(PLCamera.BslPtpProfile.DelayRequestResponseDefaultProfile);
// Set the network mode to unicast
camera.Parameters[PLCamera.BslPtpNetworkMode].SetValue(PLCamera.BslPtpNetworkMode.Unicast);
// Set the IP address of the first unicast device to 192.168.10.12
// (0xC0 = 192, 0xA8 = 168, 0x0A = 10, 0x0C = 12)
camera.Parameters[PLCamera.BslPtpUcPortAddrIndex].SetValue(0);
camera.Parameters[PLCamera.BslPtpUcPortAddr].SetValue(0xC0A80A0C);
// Enable PTP Management Protocol
camera.Parameters[PLCamera.BslPtpManagementEnable].SetValue(true);
// Disable two-step operation
camera.Parameters[PLCamera.BslPtpTwoStep].SetValue(false);
// ** Enable PTP on the current device **
camera.Parameters[PLCamera.PtpEnable].SetValue(true);
// To check the status of the PTP clock synchronization,
// implement your own check method here.
// For guidelines, see "Checking the Status of
// the PTP Clock Synchronization" in this topic.
/* Macro to check for errors */
#define CHECK(errc) if (GENAPI_E_OK != errc) printErrorAndExit(errc)
GENAPIC_RESULT errRes = GENAPI_E_OK; /* Return value of pylon methods */
/* ** Configure PTP ** */
/* Set Priority 1 to 128 */
errRes = PylonDeviceSetIntegerFeature(hdev, "BslPtpPriority1", 128);
CHECK(errRes);
/* Enable end-to-end delay measurement */
errRes = PylonDeviceFeatureFromString(hdev, "BslPtpProfile", "DelayRequestResponseDefaultProfile");
CHECK(errRes);
/* Set the network mode to unicast */
errRes = PylonDeviceFeatureFromString(hdev, "BslPtpNetworkMode", "Unicast");
CHECK(errRes);
/* Set the IP address of the first unicast device to 192.168.10.12 */
/* (0xC0 = 192, 0xA8 = 168, 0x0A = 10, 0x0C = 12) */
errRes = PylonDeviceSetIntegerFeature(hdev, "BslPtpUcPortAddrIndex", 0);
CHECK(errRes);
errRes = PylonDeviceSetIntegerFeature(hdev, "BslPtpUcPortAddr", 0xC0A80A0C);
CHECK(errRes);
/* Enable PTP Management Protocol */
errRes = PylonDeviceSetBooleanFeature(hdev, "BslPtpManagementEnable", 1);
CHECK(errRes);
/* Disable two-step operation */
errRes = PylonDeviceSetBooleanFeature(hdev, "BslPtpTwoStep", 0);
CHECK(errRes);
/* ** Enable PTP on the current device ** */
errRes = PylonDeviceSetBooleanFeature(hdev, "PtpEnable", 1);
CHECK(errRes);
/* To check the status of the PTP clock synchronization, */
/* implement your own check method here. */
/* For guidelines, see "Checking the Status of */
/* the PTP Clock Synchronization" in this topic. */
# ** Configure PTP **
# Set Priority 1 to 128
camera.BslPtpPriority1.Value = 128
# Enable end-to-end delay measurement
camera.BslPtpProfile.Value = "DelayRequestResponseDefaultProfile"
# Set the network mode to unicast
camera.BslPtpNetworkMode.Value = "Unicast"
# Set the IP address of the first unicast device to 192.168.10.12
# (0xC0 = 192, 0xA8 = 168, 0x0A = 10, 0x0C = 12)
camera.BslPtpUcPortAddrIndex.Value = 0
camera.BslPtpUcPortAddr.Value = 0xC0A80A0C
# Enable PTP Management Protocol
camera.BslPtpManagementEnable.Value = True
# Disable two-step operation
camera.BslPtpTwoStep.Value = False
# ** Enable PTP on the current device **
camera.PtpEnable.Value = True
# To check the status of the PTP clock synchronization,
# implement your own check method here.
# For guidelines, see "Checking the Status of
# the PTP Clock Synchronization" in this topic.
Other Cameras#
INodeMap& nodemap = camera.GetNodeMap();
// Enable PTP on the current device
CBooleanParameter(nodemap, "GevIEEE1588").SetValue(true);
// To check the status of the PTP clock synchronization,
// implement your own check method here.
// For guidelines, see "Checking the Status of
// the PTP Clock Synchronization" in this topic.
/* Macro to check for errors */
#define CHECK(errc) if (GENAPI_E_OK != errc) printErrorAndExit(errc)
GENAPIC_RESULT errRes = GENAPI_E_OK; /* Return value of pylon methods */
/* Enable PTP on the current device */
errRes = PylonDeviceSetBooleanFeature(hdev, "GevIEEE1588", 1);
CHECK(errRes);
/* To check the status of the PTP clock synchronization, */
/* implement your own check method here. */
/* For guidelines, see "Checking the Status of */
/* the PTP Clock Synchronization" in this topic. */
You can also use the pylon Viewer to easily set the parameters.